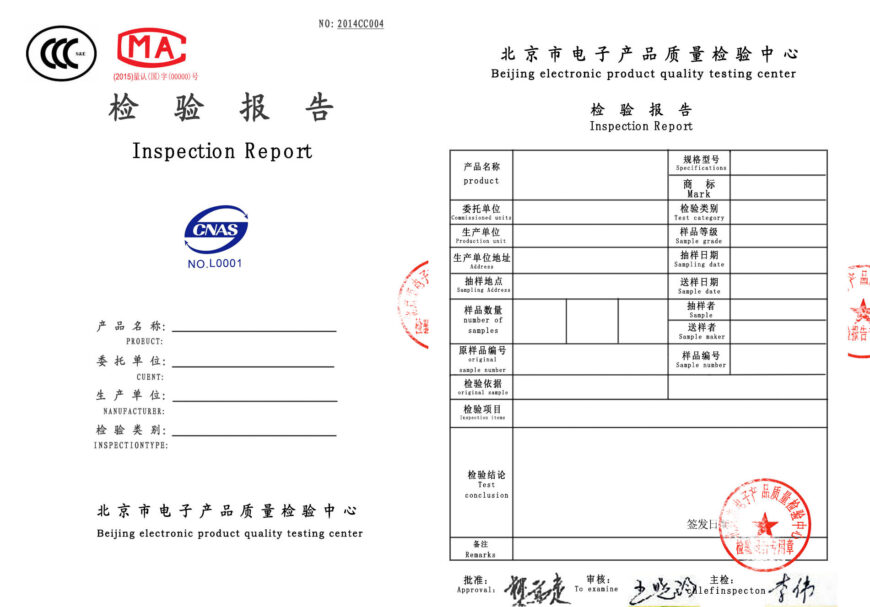
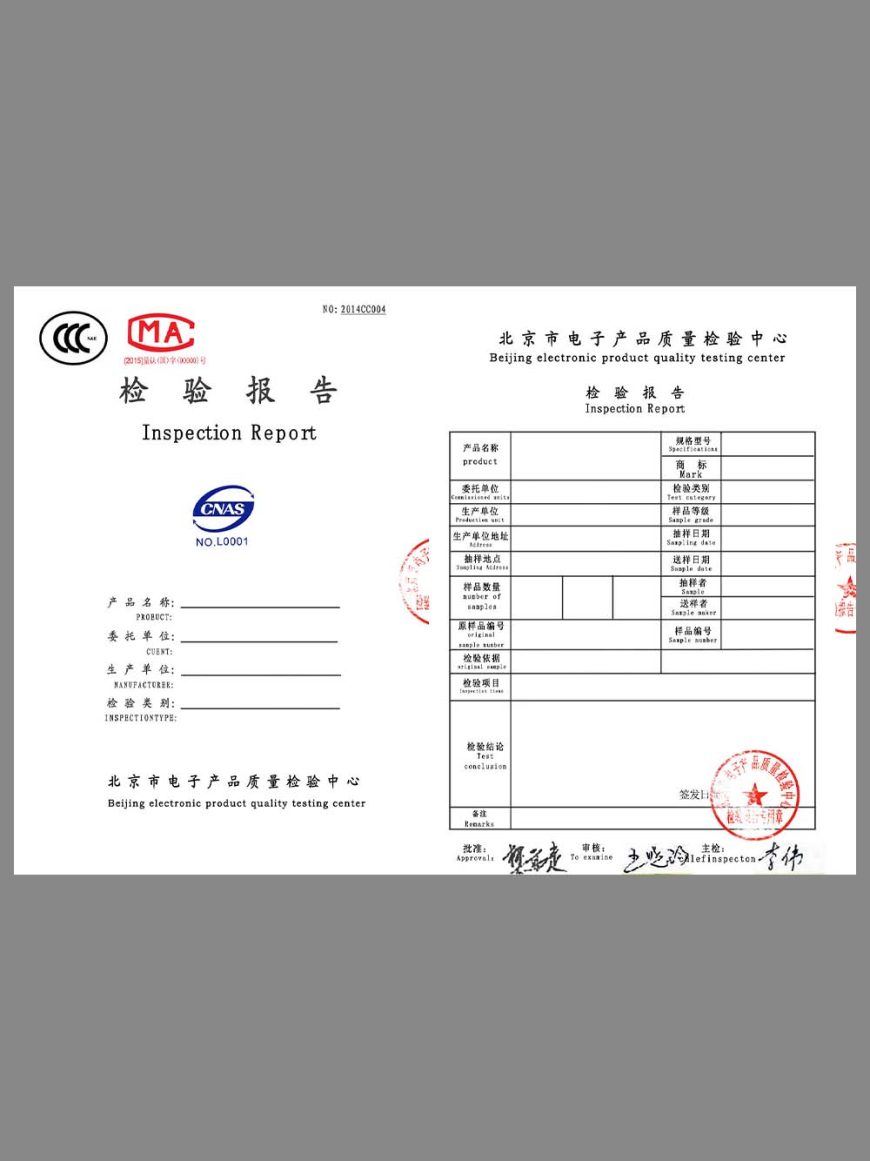
RoHs Test Report EU RoHS Testing and Certification Template
RoHs Test ReportEU RoHS Testing and Certification Template
RoHS is the “Restriction of Hazardous Substances” (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), also known as the EU RoHS Directive.The directive was enacted within the European Union in 2003 to restrict certain hazardous substances used in electrical and electronic equipment to protect human health and the environment.
The RoHS directive restricts the use of the following six hazardous substances:
1. Lead (Pb): Harmful to the nervous system, reproductive system and development, often used in the soldering process of electronic products.
2. Mercury (Hg): Harmful to the central nervous system and kidneys, often used in equipment such as fluorescent lamps and thermometers.
3. Cadmium (Cd): Harmful to kidneys and bones, often used in products such as batteries and dyes.
4. Hexavalent chromium (Cr6+): It is allergic to skin and may cause cancer. It is often used in dyeing and anti-rust treatments.
5. Polybrominated biphenyls (PBB): Potentially harmful to the environment and human health, commonly used in plastics and electronic products.
6. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE): Potentially harmful to the environment and human health, often used in flame retardants.
The RoHS directive applies to electronic and electrical equipment sold in the European market, including computers, mobile phones, home appliances, lighting equipment, etc.Manufacturers and suppliers must ensure that their products comply with the restrictions of the RoHS Directive and provide a declaration of conformity and relevant test reports.
The implementation of the RoHS directive helps reduce the use of harmful substances and environmental pollution, promotes sustainable development and increases environmental awareness.Similar hazardous substances restriction directives have also been adopted and implemented in other countries and regions.
Only products tested to comply with RoHS standards can enter the EU market.
You must log in to submit a review.